ERGONOMICS – What is it?
Derived from two Greek words: “Nomoi” meaning natural laws. “Ergon” meaning work.
Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands.
Definition:
Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between the employee and the workplace. It is a developing body of knowledge whose goal is to provide and maintain a healthy “user friendly” environment. Properly applied, ergonomic principles support each person’s desire to find a zone of individual comfort.
Benefits of Ergonomics:
- Decreased injury risk.
- Increased productivity
- Decreased mistakes/rework.
- Increased efficiency
- Decreased lost workdays.
- Improved morale
Ergonomic Concepts
- Tool design
- Workstation Design
- Visual and auditory task design
Environmental Factors
- Noise
- Vision
- Thermal
- Chemical
Psychological Stress
- Machine Pacing
- Shift Work
- Morale
Physical
- Posture
- Force
- Repetition
- Manual Materials Handling
Target Regions
- Back
- Upper Extremities
- Lower Extremities
Design and Disease
POSTURE DISCOMFORT
Standing Legs, Feet, Back
Sitting Neck, Back, Shoulders
Reaching Shoulders, Upper Arms
Head Bent Back Cervical Region
Trunk Bent Forward Lumbar Region
Static Exertions
- Holding activities
- Carrying
- Standing
- Pushing and pulling
- Arms raised.
Types of Injuries
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Numbness
- Restricted motion
- Repetitive stress injury
- Repetitive motion injury
- Cumulative trauma disorder
- Musculoskeletal disorder
Cumulative Trauma Disorders
A class of musculoskeletal disorders arising from repeated biomechanical stress due to ergonomic hazards. Common names for these disorders are:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Tendinitis
- Tenosynovitis
- Ganglion cyst
- Tennis Elbow
- Trigger Finger
- DeQuervian’s Disease
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Bursitis
- Synovitis
Cumulative Trauma Disorders
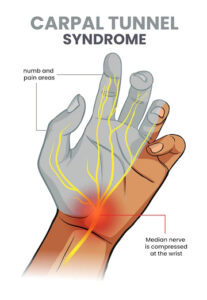
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Symptoms: numbness or tingling in thumb, index, or middle finger & ½ of ring finger; often awakened @ night by hand “falling asleep” Symptoms increased by driving or attempting to hold objects; dropping objects is a common complaint.
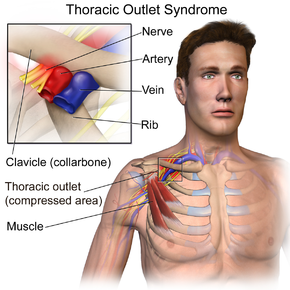
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome:
Symptoms: numbness/tingling in hand, made worse with overhead activities or cradling phone between ear and shoulder
Radial Tunnel Syndrome:
Compressed radial nerve at outside of elbow due to repetitive wrist & finger extension or turning of for arm.
Signs and Symptoms:
Sensations from elbow to base of thumb with wrist weakness a common symptom
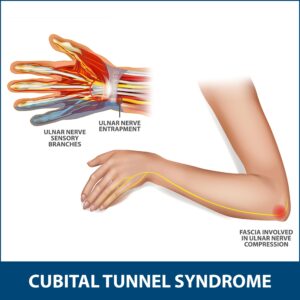
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome:
Ulnar nerve compression inside of the elbow due to repetitive bending of elbow or resting your elbow on a hard surface.
Signs and Symptoms: Numbness or tingling and inside of arm w/ tingling to ring & little fingers.
Tendons and Tendonitis
- Tendons are connective tissue that attach muscle to bone; have little stretch or rebound.
- Tendon overuse, static or prolonged position=inflammation or tendonitis
- Tendons of wrist & hand very small; at high risk for injury with overuse
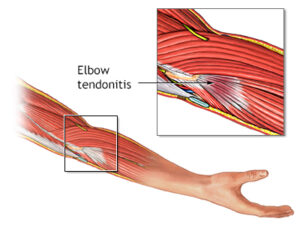
- “Tennis elbow” or lateral epicondylitis affects finger extensor tendons outside of elbow.
- “Golfer’s elbow” or medical epicondylitis affects
- Finger flexor tendons inside of elbow
Cumulative Trauma Disorders
- Synovitis – an inflammation (swelling) or irritation of a synovial lining (joint lining).
- DeQuervain’s Disease – a type of synovitis that involves the base of the thumb.
- Bursitis – an inflammation (swelling) or irritation of the connective tissue surrounding a joint, usually of the shoulder
- Cervical Radiculopathy – a compression of the nerve roots in the neck.
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment – a compression of the ulnar nerve in the wrist.
Ergonomic Risk Factors
- Repetition
- Awkward posture
- Forceful exertion
- Static posture
- Mechanical contact stress
- Temperature
- Vibration
Psychosocial Factors
- Significant Findings
- Fear of being replaced by computers
- Enlarged Jobs
- Uncertainty about job future
- Work pressure
- Lack of co-worker support
- Lack of productivity standard
- Lack of participation in decision-making
- Perception management does not value ergo.
What to do??
PREVENT, PREVENT, PREVENT!!
- Warm up & stretch before activities that are repetitive, static or prolonged.
- Take frequent breaks from ANY sustained posture every 20-30 minutes.
- Respect pain- positions or stop painful activity.
- Recognize early signs of inflammatory process, & treatment early
